How to Play Str8ts
Squares in compartments need to be filled in with single numbers. These must complete a 'straight'. A straight is a set of numbers with no gaps and in any order, such as [6,8,7] or [3,2,4,5], as shown on the diagram.
No single number can repeat in any row or column - same rule as Sudoku.
Clues in black cells remove that number as an option in that row and column, and are not part of any straight.
Need more help? Check our
Or look at the walkthrough below.
Mini Str8ts will get you started
Play today's puzzle
For further help
we have some
we have some
And we've created a special
Have a go!
Example Walk-through

In the center is a 4 in a two-cell compartment. It's complement can be 3 or 5 but there is a 5 in the black cell in the center row, so the answer is 3.
Lastly, the right-most column has a 7 which could lead to a combination from 5/6/7 to 7/8/9. To match with the horizontal two-cell compartment that has the 6 we need 5 or 7. 5 is the only possibility.

We can add 2 into the central horizontal compartment to make a straight of 2/1/3.
On the left hand side 6 is implied for the two-cell compartment that has 7 since 8 is used up vertically in the second column.

The placement of 5 might seem a little strange. But consider what has been eliminated on the row and column. 1/3/4/6/7/9 have been used up leaving 2/5/8. One of these numbers must compliment the cell to the left to make a two-cell straight. Because 7 and 9 have been used up in the row 8 is what we call a 'stranded digit'. It can't be part of a straight in the row so it can be dropped from consideration. What about the 2? A 2 would require a 1 or 3 in the vertical straight but 1 is used up. A 2/3 straight won't leave enough numbers in the rest of the row (4 and 5 remain), so 5 it is.

Now we can fill in the 8.
Where the 7 has been placed is another process of elimination. Looking at what's been used up we find 2 and 7 are possible, but vertically, the straight contains a 5, so 2 is too far away from 5 to be used, since the straight contains 3 cells.
With the 7 in place the 2 on the bottom row comes into place. We can see that only 2 and 9 remain as possibles, but 9 is rules out because of the bottom row. The straight is a long one - eight digits, but it has a 1 as a clue. So 9 is off the end of the set of possibilities. 2 is inserted.

Because so many numbers have been used we can place the 4.

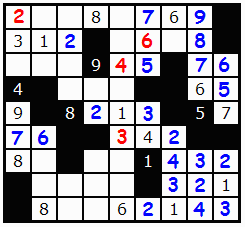
We can also plug the gap 5/?/7 in the 6th column with 6.
The 4 in the 4/5 straight is deduced from the fact that 6 is a clue in the central column. To match 5, 4 must be placed.
The 2 in the top left corner is found from the fact that only 1 and 2 remain as possibilities in that cell. But as the top row is an 8-straight and we have placed 9, 1 can't fit.

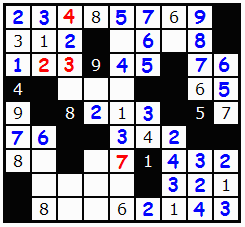
Now, to get to get to the rest of the board we need to look at the remaining cells carefully. Usually its simply a question of finding a congested cell with many numbers in the row and columns. The 7 can be placed with certainty since its the only remaining number.

We have a 1 to place in the 3d column.
That 7 placement also allows us to place the 9 above it in that column, since 7/9 were the only chances.
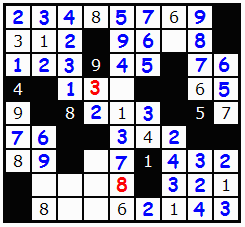
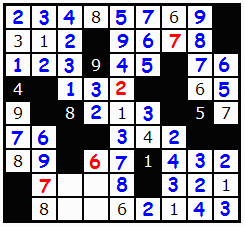
I hope this was a useful walk though, and best of luck solving Str8ts.
Andrew Stuart








Comments